Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s reproductive years. It is a significant life transition that involves several stages, each accompanied by unique hormonal changes and a range of common symptoms. Understanding these stages and their associated symptoms can empower women to better manage their health and well-being during this transformative time.
1. Perimenopause
Perimenopause, often referred to as the “menopausal transition,” typically starts in a woman’s late 30s to early 40s, though it can begin earlier or later. During this stage, the ovaries gradually produce less estrogen, causing irregular periods and a host of potential symptoms. Here are common symptoms of perimenopause:
- Irregular periods
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Mood swings and irritability
- Sleep disturbances
- Vaginal dryness and discomfort during intercourse
2. Menopause
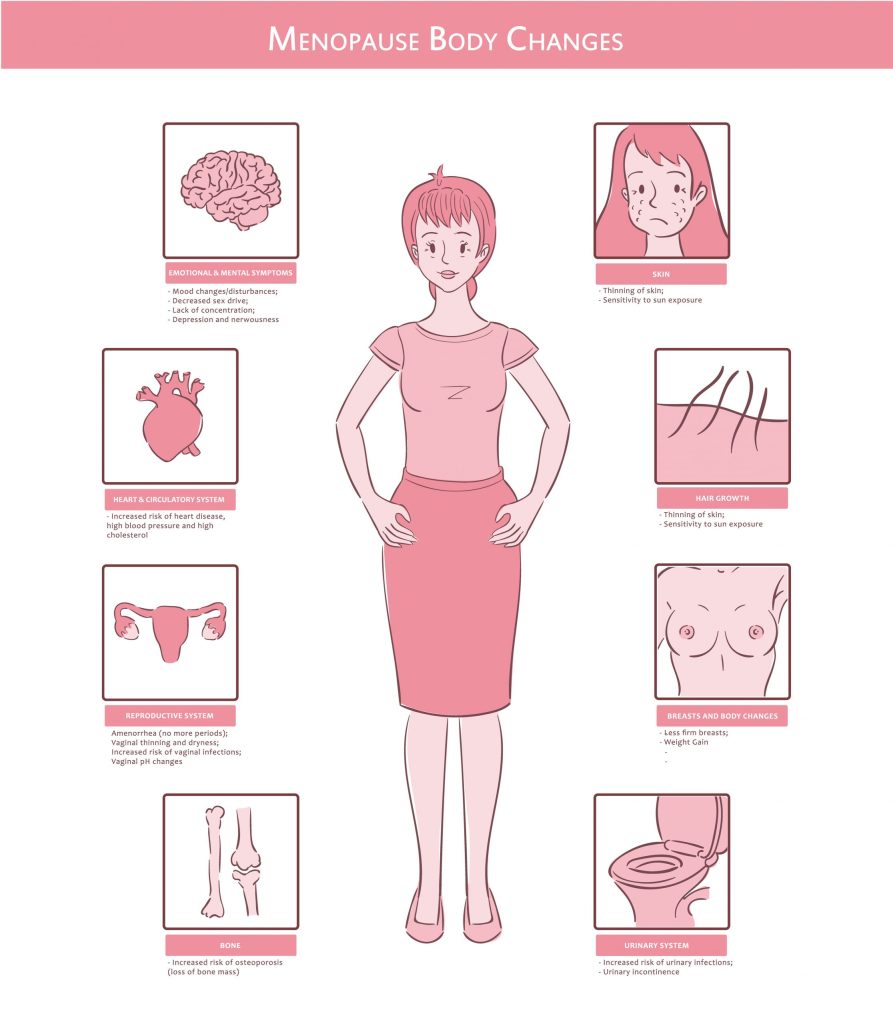
Menopause is defined as the point when a woman hasn’t had a menstrual period for 12 consecutive months. It usually occurs around the age of 50, but the timing varies for each individual. The most common symptoms during menopause include:
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Mood changes, including depression and anxiety
- Fatigue and disrupted sleep patterns
- Vaginal dryness and thinning of vaginal walls
- Changes in libido
3. Postmenopause
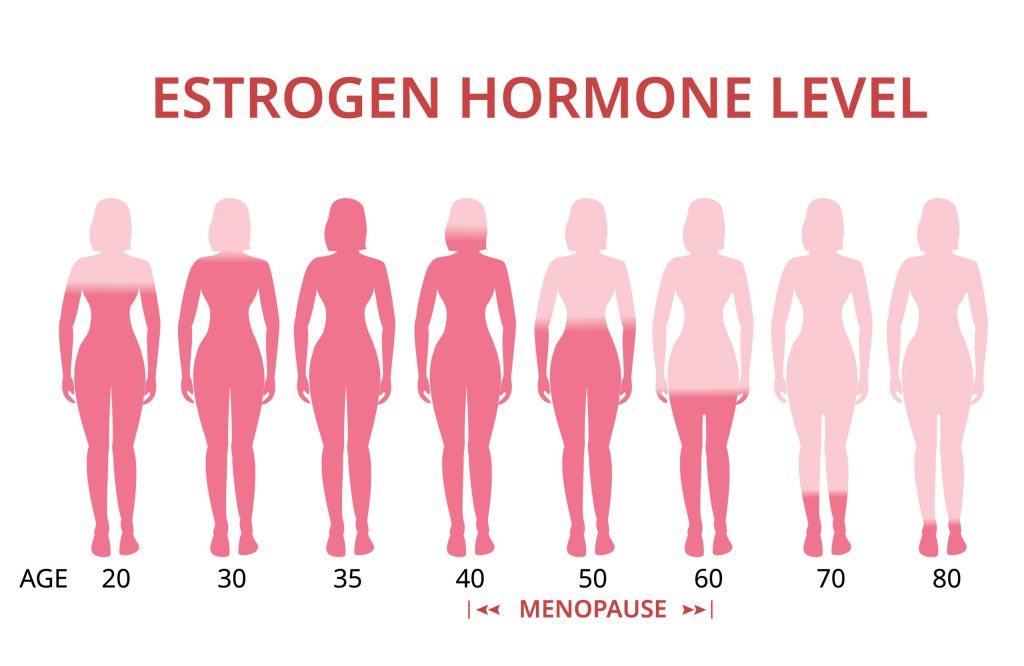
Postmenopause refers to the years following menopause. During this stage, hormone levels stabilise at lower levels, and most of the intense symptoms tend to ease. However, some symptoms may persist or arise again, such as:
- Osteoporosis risk due to decreased estrogen levels
- Heart health concerns increase as estrogen’s protective effects decline
- Continuation of vaginal dryness and discomfort
- Potential weight gain and changes in body composition
Tips for managing menopausal symptoms
- Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, engaging in regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can help mitigate the effects of hormonal changes on bone density and overall well-being.
- Stress Management: Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can alleviate mood swings and reduce stress-related symptoms.
- Medical Options: Consult a healthcare provider to discuss hormone therapy, which can help manage severe symptoms. Non-hormonal treatments, such as certain antidepressants or medications for sleep disturbances, may also be considered.
- Vaginal Health: For vaginal dryness and discomfort, over-the-counter or prescription treatments can provide relief. Regular sexual activity or the use of lubricants can also help maintain vaginal health.
- Regular Check-ups: Routine check-ups with your healthcare provider or using at-home test kits are essential to monitor bone density, cardiovascular health, and overall well-being during and after menopause.
Conclusion
Understanding the stages of menopause is beneficial not only for managing its symptoms but also for addressing your nutritional needs at each phase. It’s vital to recognise that menopause isn’t a one-size-fits-all experience, and consulting with your healthcare provider is paramount. They can offer personalised advice based on your individual health profile and test results. By making mindful lifestyle choices, seeking medical support when required, and staying educated about your body, you can approach menopause with resilience and an optimistic outlook.



